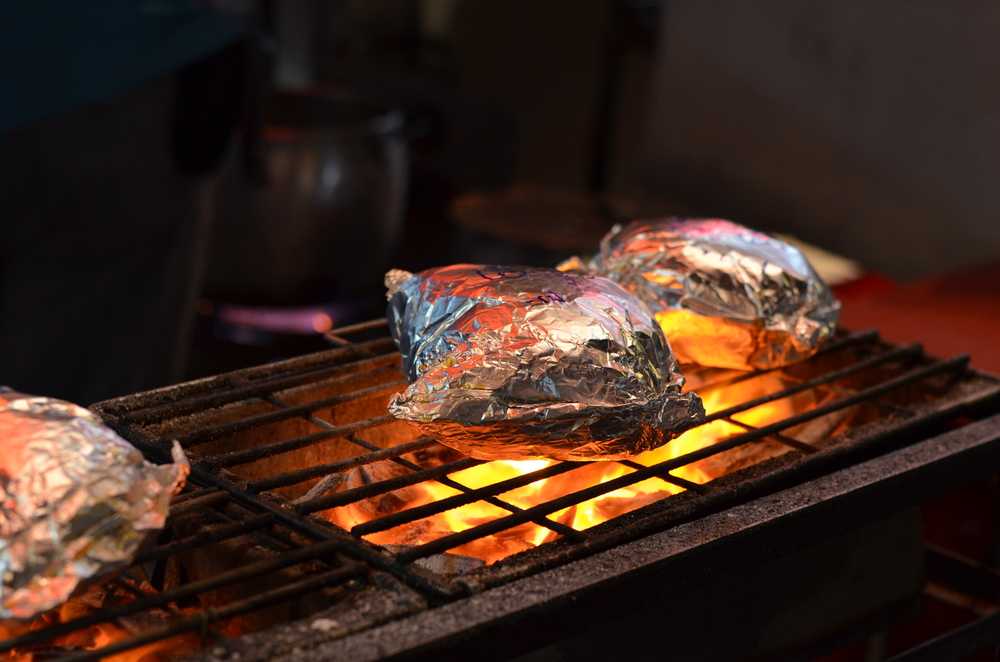
In the diverse world of culinary arts, the choice of cooking equipment plays a pivotal role in not just the taste and presentation of our meals but also in safeguarding our health. One such material that has found a permanent place in kitchens worldwide is aluminum foil. Lauded for its flexibility, heat resistance, and ease of use, cooking with aluminum foil is a practice embraced by many.
However, beneath its shiny exterior and convenient applications, aluminum foil harbors potential health risks that often go unnoticed. This article seeks to unravel the hidden dangers associated with cooking with aluminum foil, shedding light on the implications it may have on our well-being.
The widespread use of aluminum foil in cooking—from wrapping meats for a tender roast to covering dishes for a quick oven reheat—reflects its integral role in modern culinary routines. Yet, as we navigate through the various aspects of food safety and healthy living, it becomes essential to scrutinize the materials we come into close contact with, especially in our cooking processes. With emerging research pointing towards the adverse health impacts of prolonged aluminum exposure, there is a growing need to explore this topic more deeply.
The Fascinating History and Modern Use of Cooking with Aluminum Foil
The journey of aluminum foil from a scientist’s laboratory to an indispensable kitchen staple is both fascinating and reflective of human ingenuity in adapting materials for daily use. The inception of aluminum foil can be traced back to the early 20th century, with its first production credited to chemist Hans Christian Oersted in 1910. Its introduction into the culinary world, however, was not immediate; it took a few years before aluminum foil transitioned from wrapping candy and cigarettes to becoming a versatile tool in cooking. By 1913, the United States saw its first commercial production, marking the beginning of aluminum foil’s widespread application in households.
Cooking with aluminum foil gained popularity for its remarkable properties that catered to various cooking needs. Its ability to retain heat and moisture made it an ideal choice for wrapping meats, vegetables, and other food items for oven baking or grilling, ensuring evenly cooked, moist, and flavorful dishes. Beyond its use in wrapping and covering food, aluminum foil became a tool for innovative cooking methods. From crafting foil packets that infuse flavors during grilling to serving as a protective layer against direct heat, its versatility knew no bounds. This adaptability not only simplified cooking processes but also introduced a convenience that was previously unmatched, solidifying its place in kitchens around the world.
Despite its extensive utility, the shift towards scrutinizing the safety and health implications of using aluminum foil in cooking began to gain momentum. As more individuals became conscious of the materials that come into contact with their food, questions about the potential health risks associated with aluminum exposure emerged. This growing awareness has led to a reevaluation of traditional cooking practices, prompting a closer look at how aluminum foil fits into a health-conscious kitchen. The balance between convenience and safety became a central theme in discussions around cooking with aluminum foil, sparking a dialogue on its place in modern culinary practices.

Is Cooking With Aluminum Foil Safe? Unveiling the Health Implications
The question of safety in using aluminum foil for cooking purposes has sparked considerable debate among health experts and culinary aficionados alike. As a material that’s become almost indispensable in modern kitchens, understanding the health risks associated with aluminum foil is crucial.
Research has increasingly pointed towards the potential for aluminum to leach into food, particularly when it comes into contact with acidic or spicy ingredients under high temperatures. This leaching process can result in increased levels of aluminum in the food we consume, raising concerns about the long-term health effects of aluminum exposure. The potential for aluminum to accumulate in the body and contribute to a range of health issues, including neurological disorders, has led many to question: is cooking with aluminum foil safe?
The safety concerns primarily stem from studies that have observed a significant increase in the aluminum content of foods cooked in aluminum foil, with variations depending on factors like cooking temperature, time, and the acidity of the food.
For instance, cooking red meat in aluminum foil has been shown to increase its aluminum content by up to 378%, depending on the cooking conditions. Poultry isn’t exempt; it too can absorb aluminum, with increases in aluminum content ranging from 76% to 215%.
These findings are alarming because they suggest that the frequent use of aluminum foil in cooking could contribute to an increased intake of aluminum, a metal that, in excessive amounts, has been linked to health issues, including neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Given these concerns, the question of whether cooking with aluminum foil is safe becomes a matter of how it’s used and the frequency of exposure. While occasional use might not pose significant health risks, there’s a growing consensus that minimizing aluminum exposure by reducing reliance on aluminum foil, especially in cooking practices that involve high temperatures and acidic foods, could be a prudent approach to safeguarding health.
Exploring Safer Alternatives to Aluminum Foil in Cooking
In light of the concerns surrounding the safety of cooking with aluminum foil, there’s been a significant shift toward finding and using safer alternatives. These alternatives not only address health risks associated with aluminum exposure but also offer environmental benefits, aligning with a more sustainable approach to cooking and food storage. By exploring options that reduce the need for aluminum foil, individuals can make healthier choices for themselves and the planet.
- Parchment Paper: An effective substitute for aluminum foil in baking and roasting is parchment paper. It doesn’t leach chemicals into food and is heat-resistant, offering a non-stick surface ideal for various cooking tasks like lining baking sheets or wrapping items for steaming.
- Silicone Baking Mats: For an eco-friendly, reusable alternative, silicone baking mats are excellent. They withstand high temperatures and eliminate the need for disposable foil or parchment, providing a non-stick surface for baking and roasting.
- Glass or Ceramic Bakeware: These materials are non-reactive with food, offering a healthy cooking option that doubles as elegant serving ware. They’re also convenient for storing leftovers, helping to reduce the usage of disposable wraps.
- Stainless Steel Containers: Ideal for stovetop cooking and food storage, stainless steel containers are durable and free from aluminum leaching concerns, suitable for fridge or freezer storage.
- Beeswax Wraps: A sustainable, natural solution for covering and storing food, beeswax wraps are washable, reusable, and compostable, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
- Silicone Lids and Covers: Versatile and reusable, silicone lids fit various dish sizes to create an airtight seal, offering a practical solution for food storage without relying on disposable materials.
These alternatives to aluminum foil not only mitigate health risks but also support environmental sustainability, marking a shift towards safer and more eco-conscious cooking and food storage practices.

The Impact of Aluminum on Environmental Sustainability
As we delve deeper into the implications of using aluminum foil, it’s crucial to consider not just the health aspects but also the environmental impact. The production, usage, and disposal of aluminum foil contribute to a larger ecological footprint than many might realize. Understanding these impacts can guide us toward more sustainable practices, both in the kitchen and beyond.
Aluminum production is an energy-intensive process, starting from the mining of bauxite ore to its refinement into aluminum metal. This process not only consumes a significant amount of energy but also results in the emission of greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming.
Furthermore, the mining operations for extracting bauxite have been known to cause extensive environmental degradation, including deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and soil erosion. As consumers of aluminum foil, indirectly supporting these activities raises ethical and environmental concerns.
Moreover, the disposal of aluminum foil poses another challenge. While aluminum is 100% recyclable and can be recycled indefinitely without loss of quality, the reality is that a significant portion of used aluminum foil ends up in landfills. This is partly due to contamination with food residues, which complicates the recycling process, and partly due to a lack of awareness or facilities for proper recycling. In landfills, aluminum foil can take over 400 years to degrade, accumulating as long-lasting waste that contributes to landfill overflow and pollution.
Addressing these concerns starts with reducing our reliance on aluminum foil and exploring more sustainable alternatives. By making conscious choices about the materials we use for cooking and food storage, we can lessen our environmental impact and move towards a more sustainable and responsible way of living.
Reducing Aluminum Exposure: Beyond Cooking Practices
Reducing aluminum exposure extends beyond rethinking our cooking practices with aluminum foil. It involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses various aspects of our daily routines. To minimize overall aluminum intake, consider these multifaceted strategies:
- Diet and Food Choices: Prioritize fresh and whole foods over processed options to avoid aluminum-based additives. Use cookware made from materials like stainless steel, glass, or ceramics to prevent aluminum from leaching into food.
- Personal Care Products: Opt for aluminum-free deodorants and carefully read the labels of cosmetics and personal care items to avoid products containing aluminum compounds.
- Water and Environmental Considerations: Employ water filters capable of removing aluminum to reduce ingestion from drinking water. Be cautious of aluminum content in tap water, especially in areas with known high levels, and minimize the use of aluminum cans and foil for food and drink storage.
- Medications and Supplements: Seek out aluminum-free over-the-counter medications and health supplements, such as antacids and buffered aspirin, and consult with a healthcare provider for safer alternatives.
Embracing these strategies not only diminishes the potential health risks associated with excessive aluminum exposure but also supports a sustainable and environmentally friendly lifestyle. Making informed decisions about the materials we interact with daily, from the food we consume to the products we use on our bodies, is essential for our well-being and the health of the planet.
My Personal RX on Safer Cooking in the Kitchen
As a healthcare professional, I’ve seen firsthand the importance of holistic approaches to health, which include being mindful of the tools and methods we use in our kitchens. The increasing concerns regarding cooking with aluminum foil and its potential impact on our health call for a deeper understanding and a shift towards safer and more sustainable practices. It’s not just about what we eat, but also how we prepare it.
- Choose the Right Cookware: Opt for cookware that is known for its safety, like stainless steel, glass, or enameled cast iron. Avoid using damaged non-stick cookware, as it can release harmful chemicals when heated.
- Monitor Cooking Temperatures: High-temperature cooking, especially charring or burning food, can produce harmful compounds. Use cooking methods like steaming, baking, or stir-frying to prepare your food at lower temperatures where possible.
- Strengthen Your Immune System: Given the unavoidable exposure to various environmental factors that may affect our health, consider bolstering your body’s defenses with Immune Support supplements. These can provide necessary nutrients that aid in protecting and enhancing your body’s natural immune responses.
- Be Mindful of Plastic Use: Avoid using plastic containers or utensils when cooking or heating food, especially in the microwave, as they can leach chemicals into your food. Use glass or ceramic containers for heating and storing food.
- Ventilate Your Kitchen: Ensure good ventilation when cooking to avoid inhaling any fumes that might be released, particularly when grilling or frying.
- Safe Food Storage: Use appropriate food storage methods to prevent contamination and spoilage. Glass containers are a preferable option for storing leftovers, as they do not contain harmful chemicals and can be safely used for reheating food.
- Embrace a Whole Foods Diet: Minimizing processed foods reduces your exposure to aluminum additives and supports overall well-being.
- Embrace a Holistic Approach to Your Health: Engaging with a powerful guide focused on holistic health can empower you with knowledge and practices for living your best life, far beyond the kitchen.
- Regularly Detoxify Your Body: Engaging in practices that support your body’s natural detoxification processes can be beneficial, especially in a world filled with environmental toxins.
By integrating these tips into your daily routine, you’ll not only navigate the potential risks associated with cooking with aluminum foil but also take meaningful steps towards a healthier and more conscious lifestyle.
Sources:
- Bellis, M. (2019, January 28). The history of Aluminum and Charles Martin Hall. ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/charles-martin-hall-aluminum-4075554
- Đorđević, Đ., Buchtová, H., Jančíková, S., Macharáčková, B., Jarošová, M., Vítěz, T., & Kushkevych, I. (2019). Aluminum contamination of food during culinary preparation: Case study with aluminum foil and consumers’ preferences. Food Science and Nutrition, 7(10), 3349–3360. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1204
- Wpmaster. (2023, August 6). Aluminum foil the space exploration and thin film deposition. Aaluminum. https://aaluminum.com/blog/aluminum-foil-the-unsung-hero-of-space-exploration-and-thin-film-deposition/
- How aluminium is produced. (n.d.). https://www.aluminiumleader.com/production/how_aluminium_is_produced/
- familydoctor.org. (2023, March 29). Nutrition: How to make healthier food choices. https://familydoctor.org/nutrition-how-to-make-healthier-food-choices/