Swordfish is a large, predatory fish that is found in both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Although it is often referred to as a “razor-toothed” fish, swordfish are not dangerous to humans and they make a delicious and healthy addition to any diet. Swordfish are high in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which makes them a great choice for people who are looking for a healthy source of protein. They also contain high levels of vitamin B12, selenium, and phosphorus. In addition to being healthy, swordfish is also very flavorful and can be prepared in many different ways. Swordfish is a dense and meaty fish, large ones usually weigh hundreds of pounds. It also has a slightly sweet flavor and many health benefits. If you are looking for something new to add to your menu, consider giving swordfish a try!
Swordfish Health Benefits
Swordfish is Good for the Heart
Swordfish contains tons of omega-3 fatty acids and has a good ratio of that omega-6. This combination is known to help reduce inflammation and high blood pressure. Researchers have discovered that swordfish also contain good omega-3 fatty acids such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids help regulate blood pressure, which lowers the strain on the cardiovascular system and boosts heart health. It reduces the risk of stroke, heart attack, and atherosclerosis.
Swordfish is Packed with Protein
Swordfish is an excellent source of protein. Nutritionists have found that the essential amino acids found in swordfish are in sufficient amounts to help with an active metabolism. A serving of swordfish has roughly 20 grams of proteins, which are needed to maintain healthy tissues such as skin, hair, and muscles. The body uses proteins to produce enzymes and transport oxygen.
Swordfish May Reduce the Risk of Cancer
The omega-3s, vitamin D, and selenium in swordfish may help avoid cancer. Omega-3s and vitamin D have anti-inflammatory effects, which suggest that they could help prevent colorectal cancer. According to studies, both nutrients can lower the risk of colorectal cancer. (2, 3, 4, 5)
Vitamin A and folate can both cause cancerous cells to die by preventing them from reproducing. Vitamin D may also assist in the regression of new blood vessels that nourish those cells. Omega-3s likewise aid in the prevention of cancer metastasis, or the spread of cancer. Animal and human research have suggested that omega-3s might help reduce the risk of breast, prostate, and colon cancers. (7, 8)
Selenium is an antioxidant that combats the cancer-causing effects of excessive free radicals in the body. It may have a protective impact on liver, prostate, breast, and lung cancers. Selenium supplements might assist patients undergoing radiation therapy to live better lives while lowering the treatment’s unpleasant side effects. (9, 10, 11)
This study, while promising, should be taken with a grain of salt. It looks at the effects of specific nutrients rather than eating swordfish itself. As a result, further study on the consequences of swordfish is required.
Swordfish May Boost Brain Function
Vitamin D, which is present in swordfish, may benefit brain function and cognitive performance. Vitamin D promotes the development and operation of the brain. Blood and brain selenium (found in swordfish as selenoproteins) levels must be balanced for optimal mental performance and neuron survival. DHA is critical for both brain activity and improved cognition. (13, 14, 15)
Swordfish May Improve Vision
EPA and DHA are important antioxidants that protect the eyes from inflammatory eye diseases such as dry eye disease (DED) and macular degeneration (AMD). These healthy fats reduce inflammation and preserve our vision like Eye Max supplements. (12)
Swordfish Promotes Bone Strength
A single serving of swordfish will provide you with over 90 percent of the daily recommended allowance of selenium. Studies show that selenium improves bone health and strengthens teeth, hair, and nails. Selenium is an antioxidant that ensures the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
Swordfish Helps in Nerve and Muscle Support
Your muscles use magnesium to help them to contract. Plus, this same serving has nearly 10 percent of your recommended daily allowance for potassium. Potassium is a mineral that works with the sodium consumed to help keep a proper water balance in your body. If you have more sodium than potassium, you can have high blood pressure.
Swordfish Helps in Calcium Absorption
Swordfish provides nearly 100 percent of your daily requirement for vitamin D. This fat-soluble nutrient helps your body absorb calcium. It plays a role in the healthy growth of bones. Researchers and nutritionists urge the consumption of sufficient calcium amounts to stop the development of thin or brittle bones.
Swordfish Nutritional Benefits
Swordfish is a great source of niacin, selenium, B12, Omega-3, and Zinc, which are low in calories and fat.
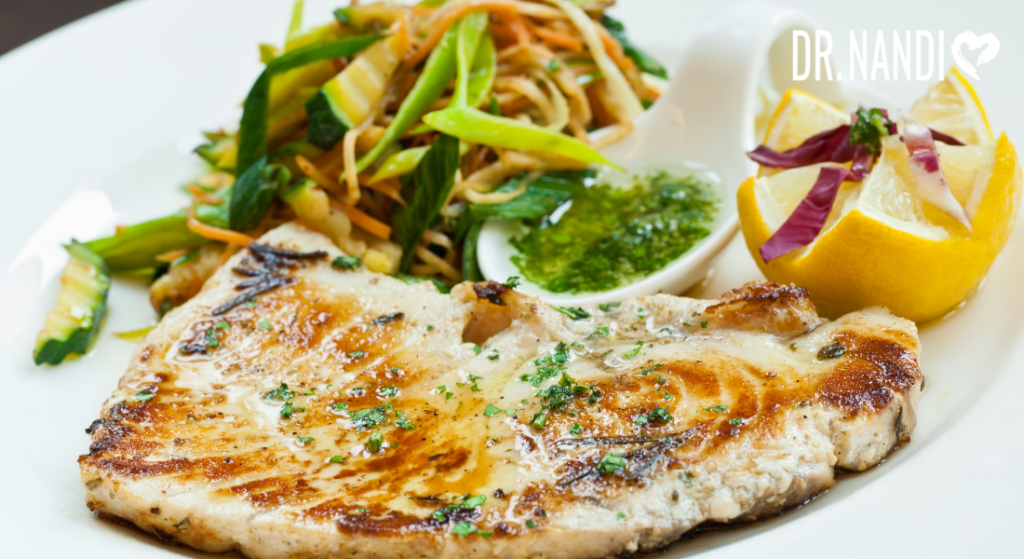
Pan Roasted Garlic Lemon Swordfish Recipe
Frequently Asked Questions
Is swordfish sustainable?
North Atlantic swordfish is one of the most sustainable seafood choices. It is fully rebuilt and one of the most environmentally responsible pelagic longline fisheries globally.
Can pregnant women eat swordfish?
Many doctors suggest not consuming swordfish if you are pregnant or nursing. Swordfish have been found to contain high levels of mercury. Mercury consumed during pregnancy has been linked to developmental delays and brain damage.
How long does swordfish last?
If you defrost swordfish in the fridge, it can be kept for an additional 1 to 2 days in the refrigerator before cooking. Swordfish thawed in the microwave or cold water should be cooked immediately. If you buy fresh swordfish, it will last up to 2 days in the fridge, but it is best eaten sooner.
Discover more ways how you can include swordfish in your daily diet. Get a FREE copy of my Superfood Cookbook.
References:
- Fish, raw, swordfish nutrition facts and analysis. (nutritionvalue.org)
- Fatty fish and fish omega-3 fatty acid intakes decrease the breast cancer risk: a case-control study | SpringerLink
- The Role of Vitamin D in Cancer Prevention | AJPH | Vol. 96 Issue 2 (aphapublications.org)
- Vitamin D: The “sunshine” vitamin – PMC (nih.gov)
- ω-3 and ω-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Obesity and Cancer – PMC (nih.gov)
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids – PubMed (nih.gov)
- ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Colonic Inflammation and Colon Cancer: Roles of Lipid-Metabolizing Enzymes Involved – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Protection against reactive oxygen species by selenoproteins – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Selenium in cancer prevention: a review of the evidence and mechanism of action – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Selenium Exposure and Cancer Risk: an Updated Meta-analysis and Meta-regression – PMC (nih.gov)
- Updates on clinical studies of selenium supplementation in radiotherapy – PMC (nih.gov)
- The Role of Fish Oil in Inflammatory Eye Diseases – PMC (nih.gov)
- The effects of vitamin D on brain development and adult brain function – ScienceDirect
- Selenium and selenoproteins in the brain and brain diseases – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan – PMC (nih.gov)











 Subscribe to Ask Dr. Nandi YouTube Channel
Subscribe to Ask Dr. Nandi YouTube Channel










